 |
 |
 |
 |
Neurotransmitters control and affect our moods, actions and health. Disrupting the lines of communication between the brain and the organ can have serious effects on our health. Inadequate neurotransmitter levels can lead to a long list of neurotransmitter-related symptoms. So What is Happening? Let's go further in the explanation, neurotransmitters have a very important role in allowing the body to work properly and sustain good mental and physical health. They help the brain balance the highs and lows of feelings and manage the hormonal signals that sent to other organs in the body. When neurotransmitters are able to work properly concentration and focus is good, we feel more directed, motivated and alive. So when the neurotransmitter levels are unbalanced these energizing and motivating signals are absent and we feel more stressed, sluggish and out--of-control.
Here a some symptoms of unbalanced signals:
- Anxiety
- Adrenal dysfunction
- Fatigue
- Poor sleep
- Loss of mental focus, or cognitive fog
- ADD and ADHD
- Addiction or dependency
- Loss of appetite control
- Compulsive behavior
- Cravings
- Low libido
- Sexual dysfunction
Adrenal hormones, sex hormones, and neurotransmitters are functionally interrelated. Changes in sex hormones and adrenal hormones can lead to neurotransmitter imbalances. In turn, neurotransmitter imbalances can affect hormone function. Including neurotransmitters with hormone panels provides a more comprehensive view of the body’s functional neuroendocrine status, this interrelationship, and the associated factors that may be contributing to symptoms.
- Good health is dependent upon balanced neurotransmitters
- Improves sleep
- Improves mood
- Improves memory
- Improves energy
- Improves sexual function
- Relieves stress
- Relieves pain
- Improves behavior fro ADHD
- Improves behavior from OCD
- Decreases addictive behaviors
- Decreases food cravings
- Helps weight loss
- Few to no side effects
Test Cost 325.00..and Prepare & go over report (1 hour) $190.00
Though there are many neurotransmitters found in the body, there are six in
particular that play significant roles in primary symptomatic conditions.
- Serotonin: involved in the regulation of sleep, mood,
appetite and aggression.
- GABA: the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the CNS,
GABA is important for balancing the excitatory actions of other
neurotransmitters.
- Dopamine: largely responsible for regulating the
pleasure/reward pathway, memory and motor control.
- Norepinephrine: involved in a wide variety of actions
including attention and focus, regulating heart rate, affecting blood flow, and
suppressing inflammation.
- Epinephrine: much like norepinephrine, this excitatory
neurotransmitter helps regulate muscle contraction, heart rate, glycogen
breakdown, blood pressure and more, and is heavily involved in the stress
response.
- Glutamate: involved in most aspects of normal brain
function including cognition, memory and learning, although high levels of
glutamate can cause excitotoxicity, a process where nerve cells are damaged by
excessive stimulation.
Neurotransmitter imbalances can be easily identified with a single,
noninvasive urine sample. Testing provides a tool to understand each patient's
specific neuroendocrine imbalances, which can be corrected with targeted
nutritional therapy, diet, and lifestyle interventions. 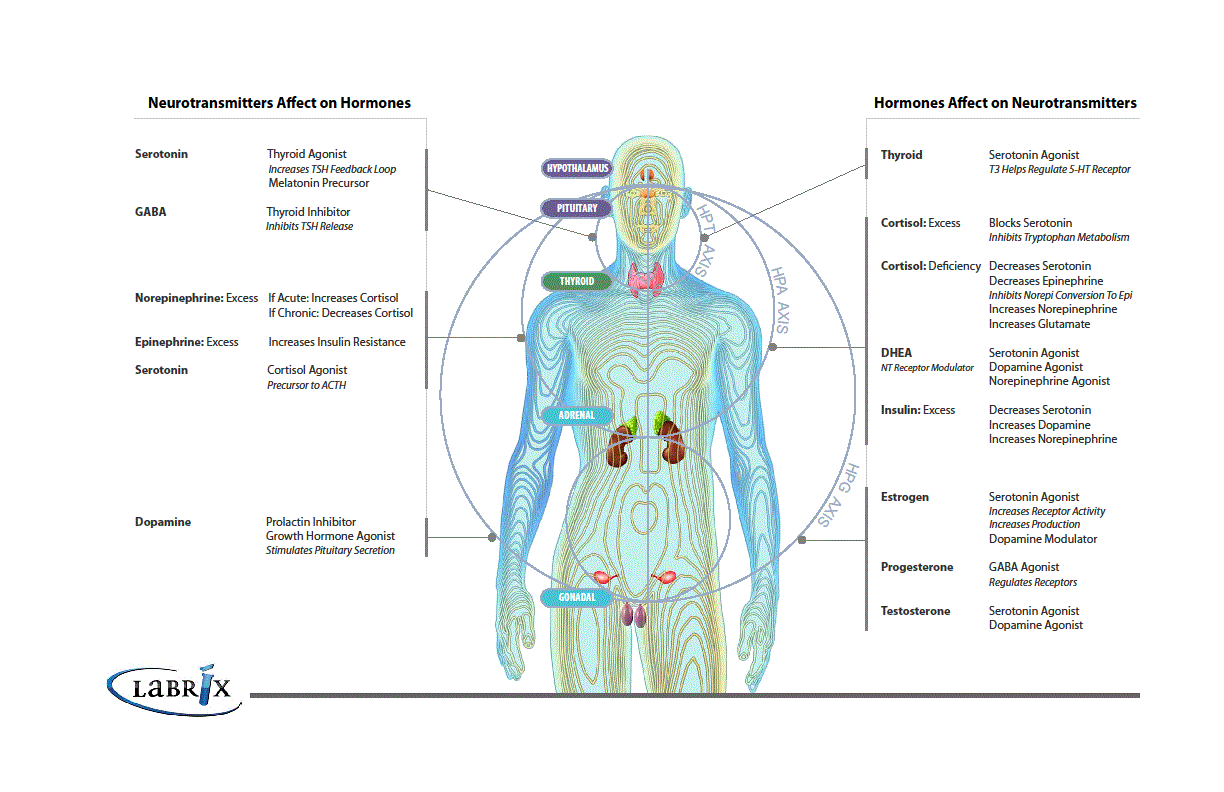
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
How to Use
Neurotransmitter imbalances can be easily identified with a single, noninvasive urine sample. Testing provides a tool to understand each patient's specific neuroendocrine imbalances, which can be corrected with targeted nutritional therapy, diet, and lifestyle interventions. Not sure which test you need? Phone consultations are available with a practitioner. How does this work? 1. Purchase online 2. Doctors order provided by us. 3. Collect urine 4. You receive the results. 5. Practitioner phone consultations available, included with test. Not available in MD.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |


|